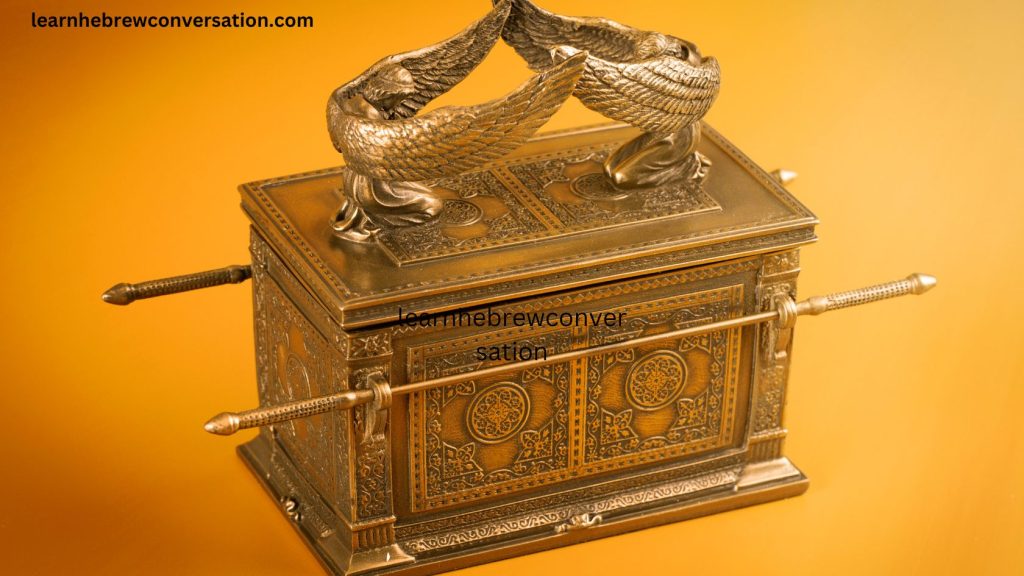
The Ark of the Covenant (Aron Habrit in Hebrew) is one of the most intriguing and sacred objects in Jewish history. This golden chest, described in detail in the Old Testament, played a central role in the religious life of ancient Israel.
Contents of the Ark- What’s Inside
The Ark’s primary contents were the two stone tablets inscribed with the Ten Commandments, given to Moses by God on Mount Sinai. Some traditions also suggest that it contained Aaron’s rod and a golden jar of manna, though biblical accounts vary on these additional items.
Construction and Design
The Ark was constructed by the Israelites according to the instructions given to Moses by God. It was made of acacia wood overlaid with gold, and it featured a gold lid known as the “Mercy Seat” or “Atonement Cover,” with two cherubim (angelic figures) facing each other with their wings spread over the cover. The Ark was carried using poles inserted through rings attached to its sides. The Ark measured approximately 4 feet long, 2.5 feet wide, and 2.5 feet high.

The ark of the covenant in the bible
More than just a container for sacred objects, the Ark symbolized God’s presence among His people. It was considered a main point of worship and played a crucial role in religious ceremonies. It was kept in the Holy of Holies, the innermost and most sacred area of the Tabernacle, and later in the Temple in Jerusalem. The Ark was carried ahead of the Israelites during their travels and battles, symbolizing God’s presence and guidance.
Historical Events Involving the Ark
The Ark features prominently in several dramatic biblical narratives.
Wanderings in the desert: The Ark traveled with the Israelites for 40 years, carried by the Levites.
Crossing into Canaan: The Ark led the Israelites across the Jordan River, whose waters miraculously parted.
Conquest of Canaan: The Ark accompanied the Israelites during their conquest, most notably in the fall of Jericho.
Placement in Shiloh: After the conquest, the Ark was set up in the Tabernacle at Shiloh.
Capture by the Philistines: During a battle in the time of Eli the High Priest, the Philistines captured the Ark.
Return to the Israelites: After causing plagues in Philistine cities, the Ark was returned to the Israelites at Beit Shemesh.
Brought to Jerusalem: King David brought the Ark to Jerusalem. Placement in Solomon’s Temple: King Solomon placed the Ark in the First Temple in Jerusalem.
Disappearance: The Ark’s fate after the Babylonian conquest of Jerusalem in 586 BCE is unknown. It was last mentioned as being in Solomon’s Temple
Disappearance and Theories
The Ark’s fate remains one of history’s great mysteries. It was last mentioned as being in Solomon’s Temple, but its whereabouts after the Babylonian conquest of Jerusalem in 586 BCE are unknown. Theories abound: some believe it was destroyed, others think it was hidden by priests, and still others suggest it was taken to Ethiopia. References in later texts like the Book of Jeremiah and 2 Maccabees have fueled further speculation.
The ark of the covenant in ethiopia
According to Ethiopian tradition, the Ark resides in the Church of Our Lady Mary of Zion in Axum, brought there by Menelik I, son of King Solomon and the Queen of Sheba, roughly 3,000 years ago. A single monk, appointed for life, guards this sacred relic, which no one else is allowed to see. While every Ethiopian church contains a replica of the Ark called a tabot, the authenticity of the original Ark’s presence remains unverified. This claim, rooted in the Ethiopian literary work Kebra Nagast, conflicts with other historical accounts and lacks concrete evidence. Despite scholarly skepticism, the belief in the Ark’s presence in Ethiopia remains a powerful element of Ethiopian Orthodox Christian faith and national identity.
The ark of the covenant in Modern Culture
The enigma of the Ark has inspired countless artistic representations and literary works throughout history. In modern times, it has featured in popular culture, most notably in the Indiana Jones film “Raiders of the Lost Ark,” which introduced the Ark’s mystique to a new generation.

The Ark of the Covenant And Aron Hakodesh
The Ark of the Covenant remains a powerful symbol of faith. The Aron Hakodesh which holds the Torah scrolls in modern synagogues serves as a symbolic continuation of the Ark of the Covenant’s role, maintaining a connection to the ancient practices of Israelite worship.